Open Heart Surgery: What You Need to Know
Introduction
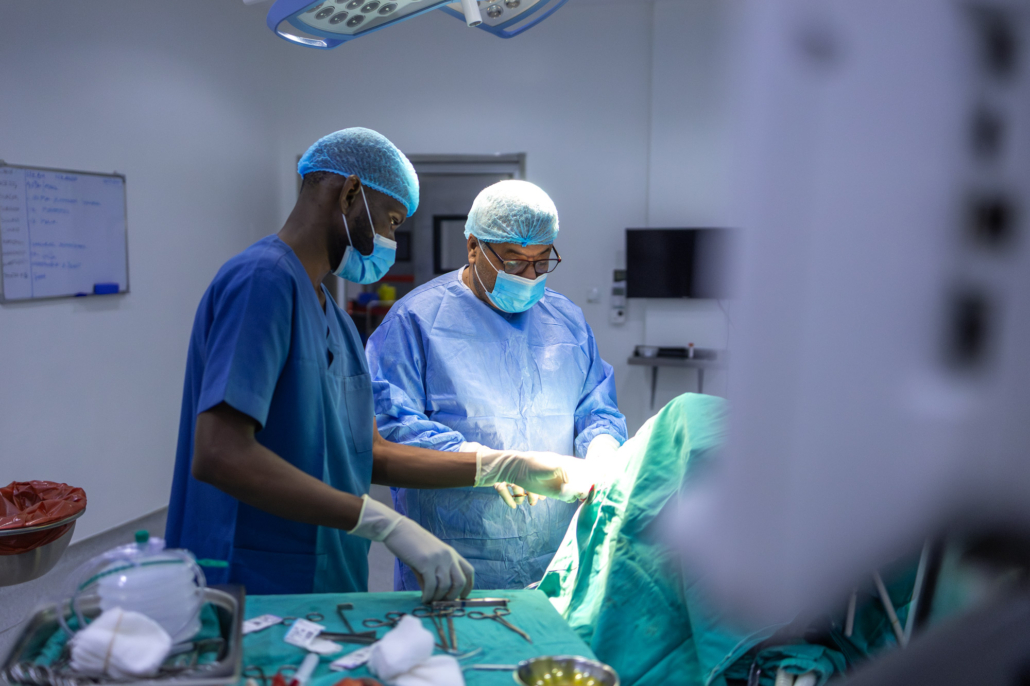
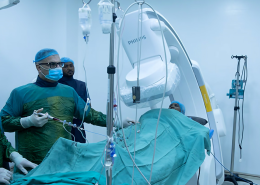
Open heart surgery is one of the most common and life-saving heart operations performed worldwide. It involves surgical procedures such as CABG (coronary artery bypass graft), valve repair, or other complex interventions carried out by a cardiothoracic specialist. This type of cardiac operation is essential for treating coronary artery disease, valve disorders, and congenital heart defects.
What Is Open Heart Surgery?
An open heart operation typically requires opening the chest and using a cardiopulmonary bypass machine to take over the function of the heart and lungs during the procedure. Patients may undergo different heart operation types, ranging from a triple bypass operation to valve repair or replacement. In some cases, procedures like angioplasty or a cardiac catheterization procedure are used as alternatives or preparatory steps.
Common Procedures
- CABG surgery (cabbage bypass): The most well-known treatment for blocked coronary arteries.
• Ascending aortic repair: Performed to address life-threatening aneurysms.
• Cardiac catheterization or heart catheterization procedures: Diagnostic and sometimes therapeutic approaches to evaluate blockages.
• Valve surgery: Often necessary for patients with severe valve disease.
Who Performs the Surgery?
Highly trained cardiothoracic specialists and cardiopathic surgeons carry out these operations in specialized centers. Many patients search online for “heart surgeons near me” to find experts capable of performing complex procedures like CABG or valve repair.
Costs and Considerations
Patients often ask about the heart replacement cost or overall expense of different surgeries. While costs vary depending on the hospital and country, procedures such as bypass or valve repair are considered major operations that require significant resources.
Recovery and Risks
Every cardiac operation carries risks, but modern surgical techniques and advances in postoperative care have greatly improved outcomes. Recovery time depends on the type of procedure—whether it’s a triple bypass, CABG surgery, or a valve operation.
Conclusion
Open heart surgery remains a cornerstone of modern medicine, giving patients with severe heart conditions a chance for longer, healthier lives. Whether undergoing a coronary artery bypass graft, valve repair, or another heart operation, patients benefit from the expertise of world-class surgeons and advanced cardiothoracic technology.